Class Of Ip Address
In the context of IPv4 addresses, IP addresses are divided into several classes based on the network bit space and the host bit space in the address. IP address classes determine the number of networks and hosts that can be hosted in each class. However, it should be noted that IP address classes are less used in modern networking practices as classless inter-domain routing (CIDR) becomes more common. However, here is an overview of the
classes of IP addresses:
Class A:
Class B:
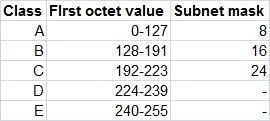
Class B addresses have the first two bits set to 10 and are used on medium-sized networks. Class B address range is 128.and 0.0.0 at 191.255.0.0. The network part occupies the first two bytes, while the other two bytes represent the host part. Class B addresses allow up to 16,384 networks and up to 65,534 hosts per network.
Class C:
Class C addresses have the first three bits set to 110 and are used on small networks. Class C address range is 192.and 0,0,0 at 223,255,255.0. The network part occupies the first three bytes, while the last byte represents the host part. Class C addresses allow up to 2,097,152 networks and up to 254 hosts per network.
Class D:
Class D addresses have the first four bits set to 1110 and are reserved for multicast addresses. Multicast addresses are used to send data to multiple devices at the same time.Class D address range is from 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255,255.
Class E:
Class E addresses have the first four bits set to 1111 and are reserved for experimental or future use. The class E address range is 240.0.0.And 0.0 in 255.255.255.254.
It should be noted that with the CIDR notation, the concept of classes of IP addresses becomes less important. CIDR allows for more flexible assignment of IP addresses using VLSM (Variable Length Subnet Masks), allowing you to partition your network into smaller subnetworks of different sizes, regardless of the original class network limitations.
In summary, IP address classes have been used to classify IPv4 addresses into different ranges depending on the network and hosting party. However, with the widespread adoption of CIDR, IP address classes are less used in modern networking practices.
Free Software Download Click Now
IP ایڈریس کلاس کی عبارت ہے ہے IPv4 نیٹ ورکنگ میں استعمال ہوتی ہے۔ IP ایڈریس کلاس یکساں سرکاری ہوتی ہیں جو ایک نیٹ ورک میں ایکساٹا ایک جیسی تناسب سے ملکر بنائی جاتی ہیں۔
IPv4 کے لحاظ سے، IP ایڈریس 5 کلاسوں میں تقسیم کی جاتی ہیں: A، B، C، D، اور E۔ ہر ایک کلاس کی رینج ایکسٹاکٹا ہوتی ہے۔
دیے گئے نیچے ہر کلاس کی تفصیلات ہیں:
- A کلاس: A کلاس کی رینج 1.0.0.0 سے 126.0.0.0 تک ہوتی ہے۔ یہ کلاس بہت بڑی نیٹ ورکس کے لئے مختص ہوتی ہے اور ہر نیٹ ورک میں 16 ملین ہوسٹز کا سپورٹ کر سکتا ہے۔
- B کلاس: B کلاس کی رینج 128.0.0.0 سے 191.255.0.0 تک ہوتی ہے۔ یہ کلاس درمیانی سائز کے نیٹ ورکس کے لئے مختص ہوتی ہے اور ہر نیٹ ورک میں 65,536 ہوسٹز کا سپورٹ کر سکتا ہے۔
- C کلاس: C کلاس کی رینج 192.0.0.0 سے 223.255.255.0 تک ہوتی ہے۔ یہ کلاس چھوٹے سائز کے نیٹ ورکس کے لئے مختص ہوتی ہے اور ہر نیٹ ورک میں صرف 256 ہوسٹز کا سپورٹ کر سکتا ہے۔
- D کلاس: D کلاس کی رینج 224.0.0.



Comments
Post a Comment